What is AI (artificial intelligence)?
- Artificial Intelligence November 17,2024

Artificial Intelligence: Machines That Think Like Humans
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as one of the most transformation technological advancements of the 21st century. At its core, AI refers to the ability of machines to mimic human cognitive functions such as reasoning, learning, problem-solving, perception, and creativity. These capabilities, once limited to science fiction, are now integral to modern life, driving innovations across industries and reshaping how we interact with technology.
The concept of machines assisting humans is not new. Since the invention of the wheel, tools and devices have amplified human productivity, enabling us to achieve tasks that would otherwise be impossible. Machines have evolved alongside us from simple levers to intricate robotics. But the leap into artificial intelligence, where machines not only execute tasks but also “think,” represents a paradigm shift.
Yet, with great advancements come great questions. How will intelligent machines shape our future? Will they remain tools in our hands, or could they evolve to operate independently? These questions are central to understanding the journey of AI and its implications for humanity.
Artifical Intelligence
The Rise of AI: From Concept to Reality
The journey of artificial intelligence began long before the term was coined in 1956 by computer scientist John McCarthy during a workshop at Dartmouth College. However, the groundwork for this revolutionary field was laid decades earlier by pioneers like Alan Turing. In 1950, Turing introduced the concept of the “imitation game,” now famously known as the Turing Test. This test evaluates whether a machine can exhibit intelligent behavior indistinguishable from that of a human.
In the 20th century, theoretical ideas about AI began to take shape. The development of early computing systems provided the tools necessary for researchers to explore the possibilities of machine intelligence. By the 1970s, practical applications such as personal calculators brought AI into everyday life. Fast forward to the 21st century, and AI is no longer a theoretical concept—it is an integral part of our daily lives.
Today, AI powers technologies like voice assistants, autonomous vehicles, personalized recommendations, and customer service ai chatbots. These systems are capable of performing complex tasks at speeds and scales that humans cannot match. For example, modern AI systems can analyze vast datasets in seconds, enabling breakthroughs in fields like medicine, finance, and logistics.
The Building Blocks of Artificial Intelligence
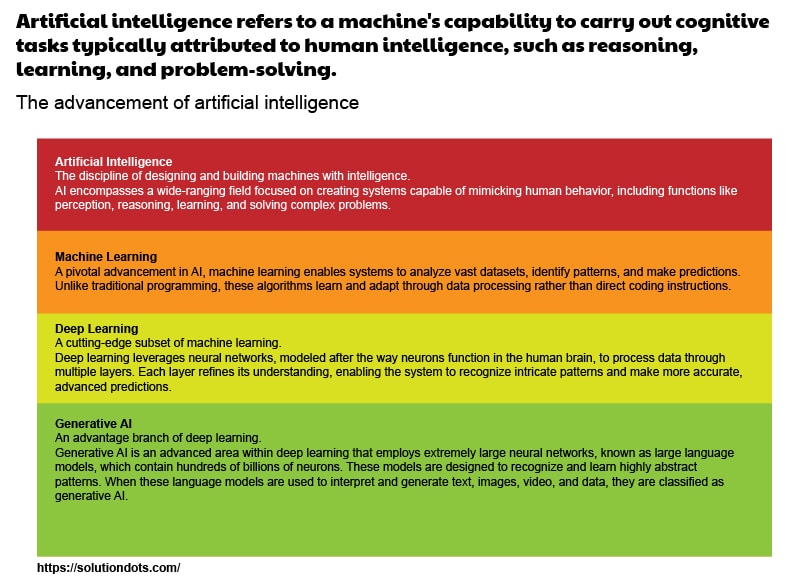
1. Machine Learning: The Backbone of AI
Machine learning (ML) is a subset of AI that enables machines to learn from data and improve over time without explicit programming. By analyzing patterns in large datasets, ML algorithms can make predictions, identify trends, and automate decision-making.
- How It Works: Machine learning models are trained on historical data to recognize patterns. Once trained, these models can process new inputs and provide accurate results. For instance, spam filters use machine learning to identify and block unwanted emails.
- Applications: ML is used in diverse industries, from healthcare (for diagnosing diseases) to finance (for detecting fraudulent transactions). Retail companies use ML to recommend products based on customer preferences, while transportation networks optimize routes using real-time data.
2. Deep Learning: Advancing Machine Learning
Deep learning, a more advanced form of machine learning, is inspired by the structure and function of the human brain. It uses neural networks with multiple layers to process complex data and make sophisticated predictions.
Examples: Deep learning powers applications like image recognition, speech-to-text conversion, and natural language processing (NLP). For example, deep learning algorithms enable virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa to understand and respond to voice commands.
How It Works: Neural networks process information through layers of interconnected nodes, similar to neurons in the brain. Each layer extracts specific features from the data, enabling the system to recognize intricate patterns.
Generative AI: Creating Something New
Generative AI is a groundbreaking subset of AI that focuses on creating new content based on learned patterns. Unlike traditional AI, which analyzes and interprets existing data, generative AI produces original outputs, such as text, images, music, or videos.
- Key Tools: Popular generative AI tools include ChatGPT, which generates human-like text, and DALL-E, which creates artwork based on textual descriptions.
- Applications: Generative AI has vast potential across industries. In marketing, it can create personalized ad copy. In entertainment, it can develop scripts and storylines. In design, it can generate visual prototypes based on user inputs.
Although generative AI is still in its infancy, its ability to produce creative outputs marks a significant leap forward in AI capabilities. However, it also raises ethical concerns, such as the risk of misinformation, plagiarism, and bias in generated content.
AI Applications: Transforming Industries
AI has become a cornerstone of innovation, driving advancements in multiple sectors:
Entertainment: Streaming platforms use AI to recommend content tailored to individual preferences. Generative AI creates realistic visual effects, transforming movie production.
Healthcare: AI is revolutionizing diagnostics, treatment planning, and drug discovery. Machine learning models analyze medical imaging to detect diseases like cancer with high accuracy. AI-powered systems also assist in managing patient records and predicting health outcomes.
Finance: Banks and financial institutions leverage AI to detect fraudulent activities, assess credit risks, and automate customer service. Robo-advisors use AI to provide personalized investment strategies.
Education: AI-powered platforms offer personalized learning experiences, adapting to students’ strengths and weaknesses. Virtual tutors and language learning apps make education more accessible.
Transportation: Autonomous vehicles, powered by AI, are transforming mobility. AI optimizes traffic management, reducing congestion and improving safety.
Retail: AI enhances customer experiences through personalized recommendations, chatbots for customer support, and inventory management systems.
AI Ethics: Navigating Challenges and Risks
Despite its transformative potential, AI presents several challenges:
- Bias and Fairness: AI systems can inherit biases from training data, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. Addressing these biases is crucial for ethical AI deployment.
- Misinformation: Generative AI can produce convincing yet false information, raising concerns about misinformation and deepfake content.
- Privacy and Security: AI systems often require vast amounts of personal data, increasing the risk of privacy breaches. Robust data protection measures are essential.
Organizations adopting AI must prioritize transparency, accountability, and inclusivity. Governments and regulatory bodies are also stepping in to ensure responsible AI usage through frameworks like the AI Bill of Rights.
Artificial General Intelligence: A Distant Horizon
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) refers to AI systems that can perform any intellectual task that a human can. Unlike narrow AI, which is designed for specific tasks, AGI would possess human-like reasoning, creativity, and adaptability.
While AGI remains a theoretical concept, its realization could revolutionize society, enabling machines to solve complex global challenges. However, experts predict that AGI is still decades—if not centuries—away. Until then, the focus remains on advancing narrow AI and exploring its potential.
The Road Ahead: Scaling AI for the Future
As AI continues to evolve, organizations must adapt to fully leverage its potential. This involves breaking down silos, fostering interdisciplinary collaboration, and scaling AI initiatives across business functions.
Agility and Innovation: Adopting an agile mindset helps organizations experiment with AI applications, learn from failures, and scale successful initiatives.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration: AI projects thrive when diverse teams collaborate, combining technical expertise with domain knowledge.
Empowering Decision-Making: AI can enhance decision-making by providing data-driven insights, but human oversight remains critical to ensure ethical outcomes.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence has moved from the realm of science fiction to an indispensable tool in modern life. Its ability to mimic human cognition has unlocked unprecedented opportunities across industries, enabling faster decision-making, improved efficiency, and innovative solutions to complex problems.
However, as AI becomes increasingly embedded in society, its ethical implications cannot be ignored. Ensuring fairness, accountability, and inclusivity in AI systems is crucial for building trust and maximizing its benefits.
As we look to the future, the possibilities of AI are boundless. By embracing this transformative technology responsibly, humanity can shape a future where intelligent machines complement human ingenuity, driving progress and innovation for generations to come.









 Saudi Arabia (English)
Saudi Arabia (English) United Kingdom
United Kingdom Global Site
Global Site