Why You Need to Switch on Cloud ERP Technology?
- ERP (Cloud) September 21,2023

An Introduction to Cloud ERP
According to WhatIs.com, cloud ERP is a tactic of enterprise resource planning (ERP) that make use of cloud computing platforms and services by making your business process more flexible and easier business transactions.

At SolutionDot, we like take Cloud ERP and Cloud Accounting Software’s as tools to give a boost for both medium and small businesses. Our Cloud suite is basically designed and developed with that target in mind.
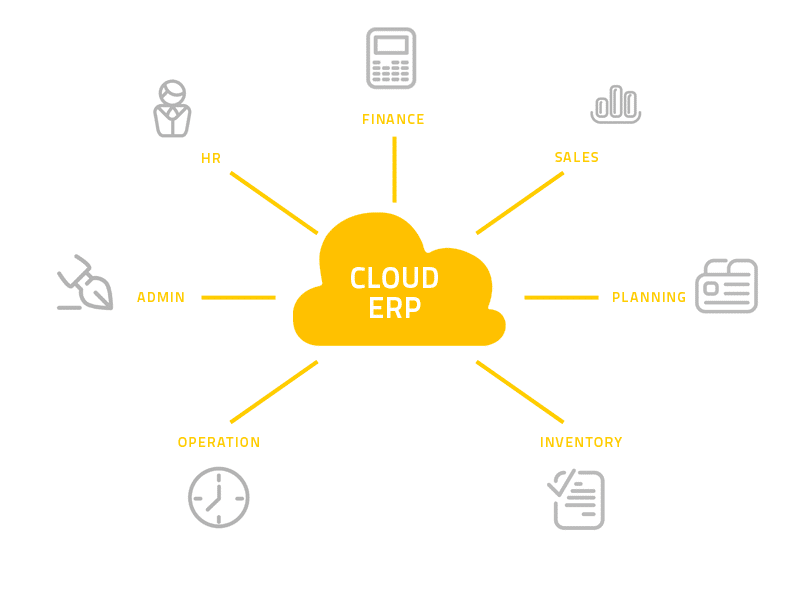
Most of the organizations invest in HR, Investment, Supply Chain, Payroll, and other Inventory systems that are core parts of the ERP.
SolutionDots’ Cloud ERP core areas includes, empowering your people, ease to control business and adding new strengths to your organization. It adds more growth in your profit graph and provide ease your employees to work from anywhere, anytime through any device.
Why Cloud Computing Matters?
Though there is a list of advantages that are strongly in the favor of cloud computing. That actually makes your mind about its importance and its worth.
Cloud based ERP profits its customers by cutting down hardware cost and offering applications’ scalability features. For more information, read Top 14 Ravishing Advantages of Cloud Computing.
In addition, cloud computing technology has made quite easy for SolutionDots to deliver ERP as SaaS (Software as a Service) for our valued customers who are interested to attain ERP.
Customers can build their own internal cloud in order to lower down current hardware cost and getting more control on the integration features with local access to their data server.
Web Technology Is Critical To Cloud Computing
Web technology permits customers to use their browsers to contact their business application.
- Definition of Web-Based Software’s
The use of browser (Thin Client) to access an application (Software Application) through internet/intranet to accomplish work.
Customers receive many benefits by using web-based software’s, which are actually not inherently a part of the cloud. Customers save both money and time of software installation and maintenance while eliminating it from client sides. Web provide ease to access from any device independent of platform specification.

Web provide Independent remote access to applications without expensive and complicated VPN code. Finally SolutionDots’ web-based solutions are all manageable from central database structure.
This feature in short provides guarantee that all users can contact in real-time with data neglecting their current position.
When an organization has multiple stations, the benefits of web software’s automatically get more noteworthy in their nature.
- Hosted Clouds
Vendors usually claim to have ‘cloud based ERP solutions’ when they place legacy software on hosted virtual server. Customer avails fewer benefits without web based software described here.
For bulk client’s occurrence you frequently required long installation times, dispersed data, clients’ upgrades and complicated remote access software. When you are looking for cloud ERP software, make sure that it is web-based!
The below table is summarizing the key benefits:
| Key Benefits of . . . | ||
| Web Technology | SaaS (s/w as service) | Cloud Technology |
| Access from anywhere. No IT resource required. Pay only for usage. | No software to install & upgrade. Minimal capital expenditures. Scale resources quickly. | Cross platform compatibility. Automatic updates and upgrades. Switch from on-premise to SaaS. |
Addressing the Conflicts in The Cloud
There are some terminologies and requirements, introduced by vendors and advocates which have been disputed as a source of being a true cloud environment.
- Multi-Tenancy
Multitenancy is refer to a software architecture in which a single instance of a software run on a server and serves (multiple customers) as a multiple tenants. Each customer is called as ‘Tenant’.
Some cloud ERP merchants claim that multiple users, must share the same software in order to qualify as a cloud application. SaaS claims that they can lower down cost of up gradation and product updates by this kind of infrastructure.
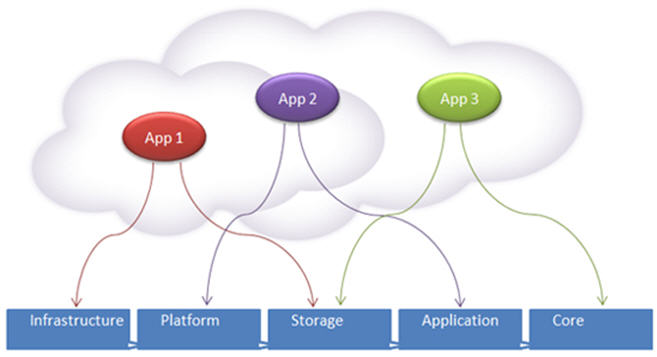
Multi tenancy can occur at different levels, like infrastructure, platform and application level. The accommodation among flexibility and cost are easily justifiable in both multi-tenant infrastructure and platform.
Multitenancy is only favorable at the application layer and make cost of software lower than the need of its flexibility.
- Internal Clouds
A multinational organization can own a single server or as many as servers as a cloud datacenter. In this scenario, it is hard to claim that cloud cannot be hosted inside. Although if an organization have single server, than its capacity level will become limited.
So here the definition of cloud, according to the NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) could be challenged. Between these two extreme levels, there is a gray area where experts debate about should we called internal deployment as cloud or not?
- Hosted Vs. Cloud
Hosting is another form to outsource IT operations. As defined above, hosting is only operative if the software does not hold any client components.
A Pure Definition of Cloud ERP
Cloud ERP is (Enterprise Resource Planning) a software that is presented on a platform over the Internet.
The use of the word “Cloud” includes a wide-ranging set of applications and software deployment models, namely SaaS (Software-as-a-Service).

After assembling numerous online resources, we formed a generally accepted definition of cloud computing.
Definition of Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing is a way to access software and hardware and other resources through the internet provided on demand, in order to accomplish work and other business task.
You can read, the more detailed definition of cloud computing according to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
The bottom line is that, ERP software that is positioned in a cloud environment becomes a ‘Cloud ERP Software’. Most of the cloud environments are built using visualization, load balancing technologies. That permits applications to deploy on multiple servers and database resources.









 Saudi Arabia (English)
Saudi Arabia (English) United Kingdom
United Kingdom Global Site
Global Site